What Are Internal Links?
An internal link is a hyperlink that points from one page on your site to another page on the same domain.
Internal links connect relevant web pages or related content, helping users and web crawlers navigate a website.
These links use descriptive anchor texts to describe the page being linked to. For example, take a look at the internal link shown in the image below:
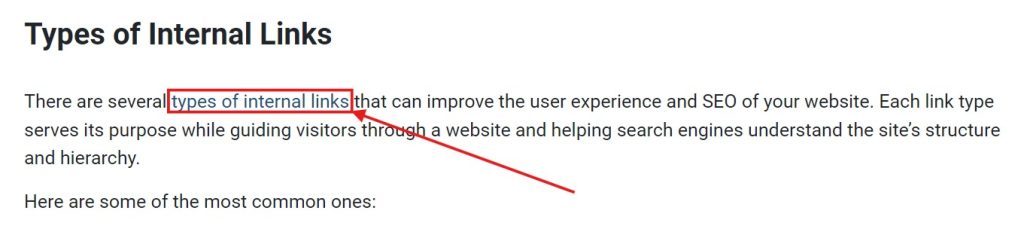
Based on the anchor text used, clicking the link will take users to a resource explaining and enumerating the different internal link types.
Here is what the HTML source code looks like for the internal link:
<a href="https://linkstorm.io/resources/the-different-types-of-internal-links" target="_self" >types of internal links</a>Internal links are essential to help users and search engines discover different pages on your site that are relevant to the current page.
For instance, a user reading an article on “how to lose weight” may click internal links to relevant pages on the current topic, such as “low-calorie meals” or “high-intensity interval training.”
There’s more to internal links than just navigation. Below, we’ll uncover why internal links are important for SEO and explore tips on how to use internal links to serve your overall SEO strategy.
Internal links vs. external links vs. inbound links
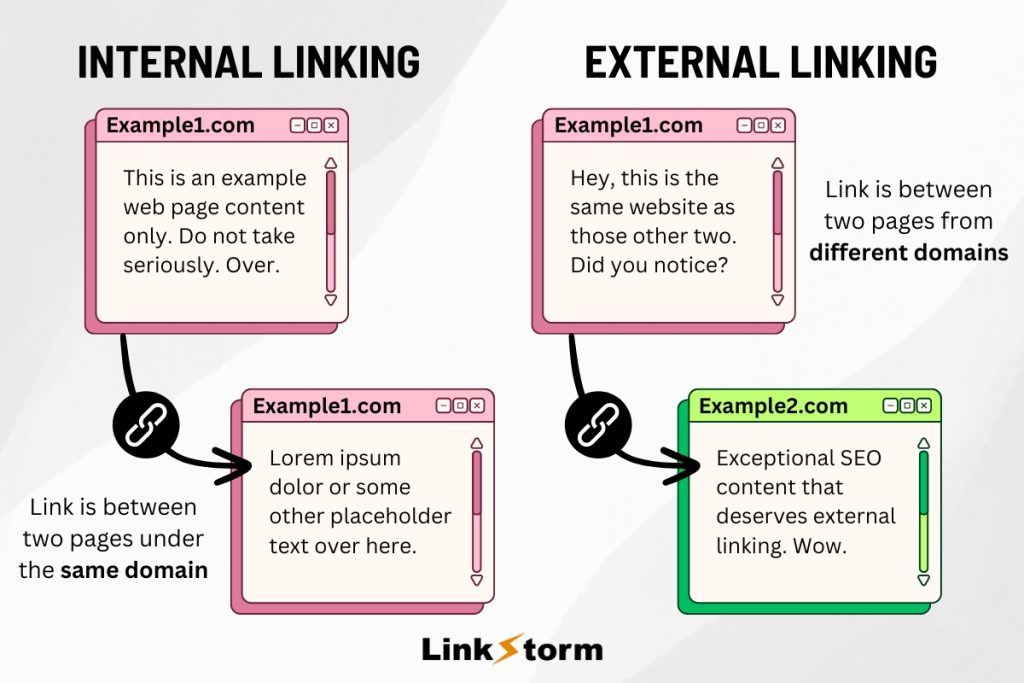
Internal links connect different pages on the same domain. When users click internal links, they get sent to a different page but do not exit the website.
Conversely, external links, or “outbound links,” link to pages on other websites. Users who click external links exit your website and are sent to a page on a different domain. Take a look:
Related content: Internal links vs External Links: Differences & SEO Benefits
Inbound links, more famously known as “backlinks,” are also different. These backlinks are hyperlinks from external websites pointing to pages on your website, as seen below:
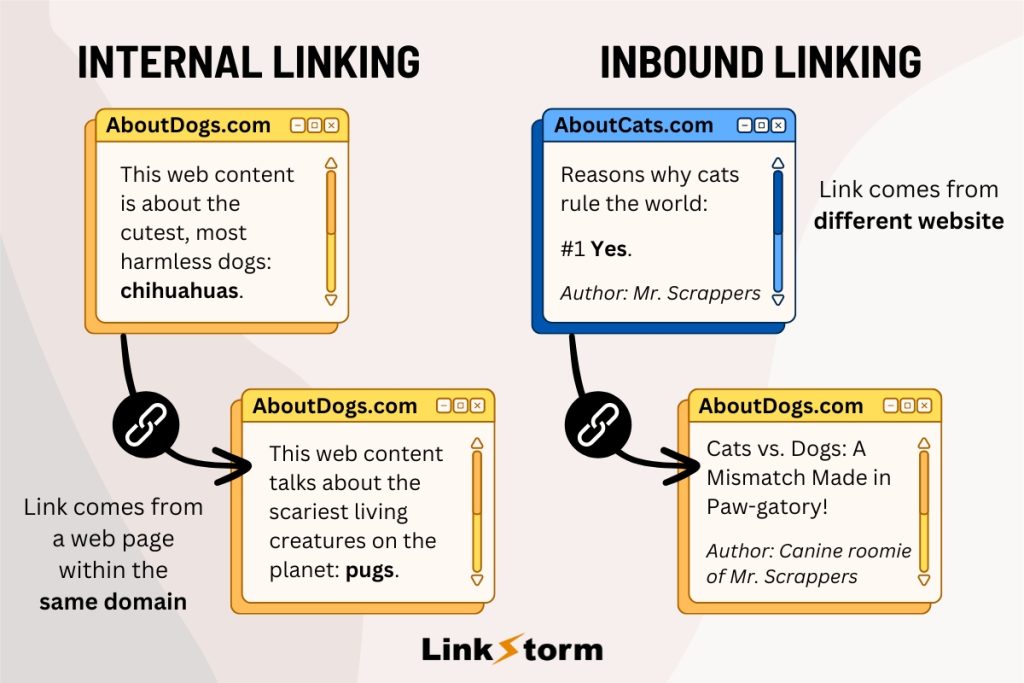
Related content: Internal Links vs Inbound Links: Pros & Cons for SEO
How Do Search Engines Use Internal Links?
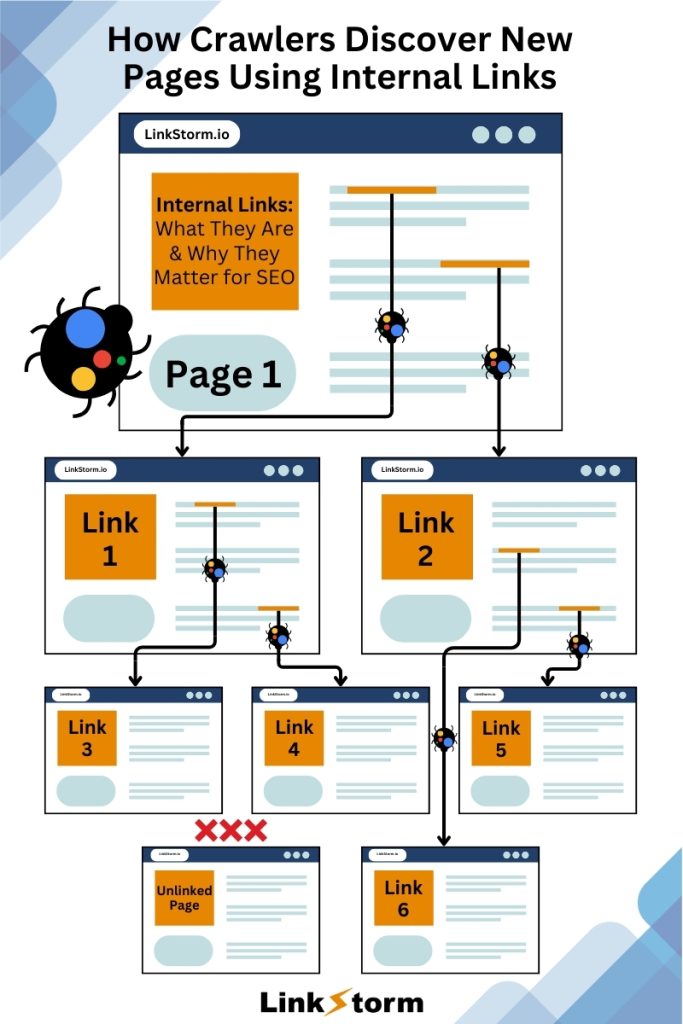
Search engine crawlers, like Googlebot, depend on internal links to crawl, discover, and index pages on a website.
To understand this better, it’s essential to know the two major types of internal links:
- Structural links
- Contextual links
Structural links are the foundational internal links that establish the site architecture and define its hierarchy. These links include the main navigation menu, footer links, and sidebar menu.
From the homepage, Googlebot uses structural links to efficiently navigate a website’s main sections, ensuring that critical areas are regularly visited and indexed.
Ideally, the site architecture must be arranged like a pyramid, with the homepage at the very top, as it is the strongest page on the website and the starting point of a search engine’s crawling activity.
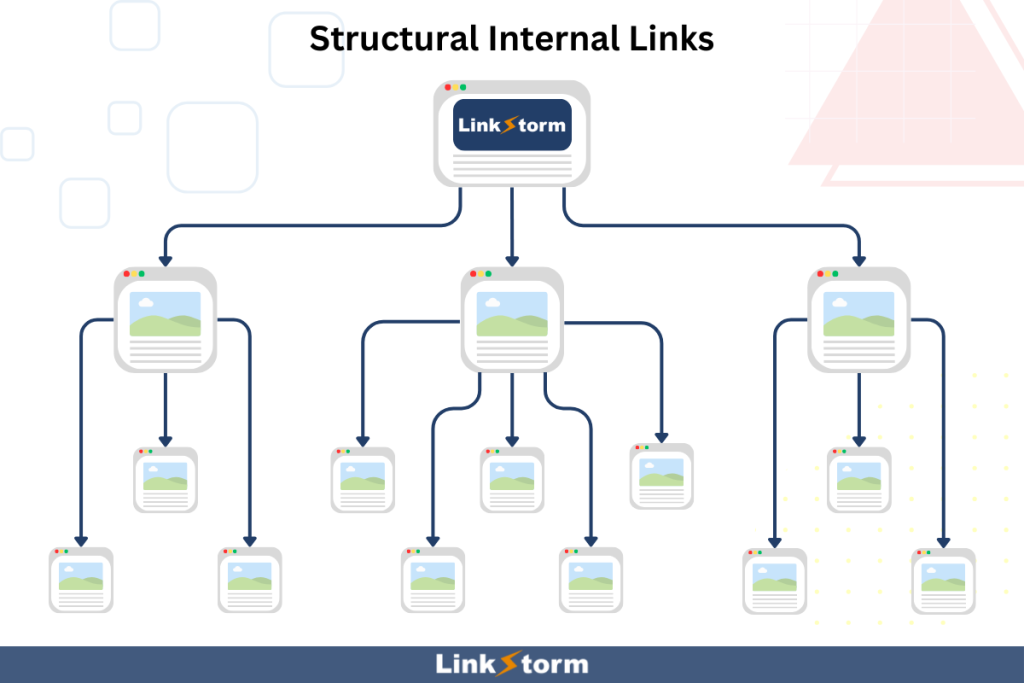
Search engine crawlers also use structural internal links to comprehend the overall architecture of the site, highlighting which pages are most critical. Pages linked from the homepage or the main navigation menu are viewed as more important in the site’s hierarchy, resulting in higher search rankings.
On the other hand, contextual links are embedded within a page’s content or body text. These links point to related pages or posts, often based on the topic discussed in the content.
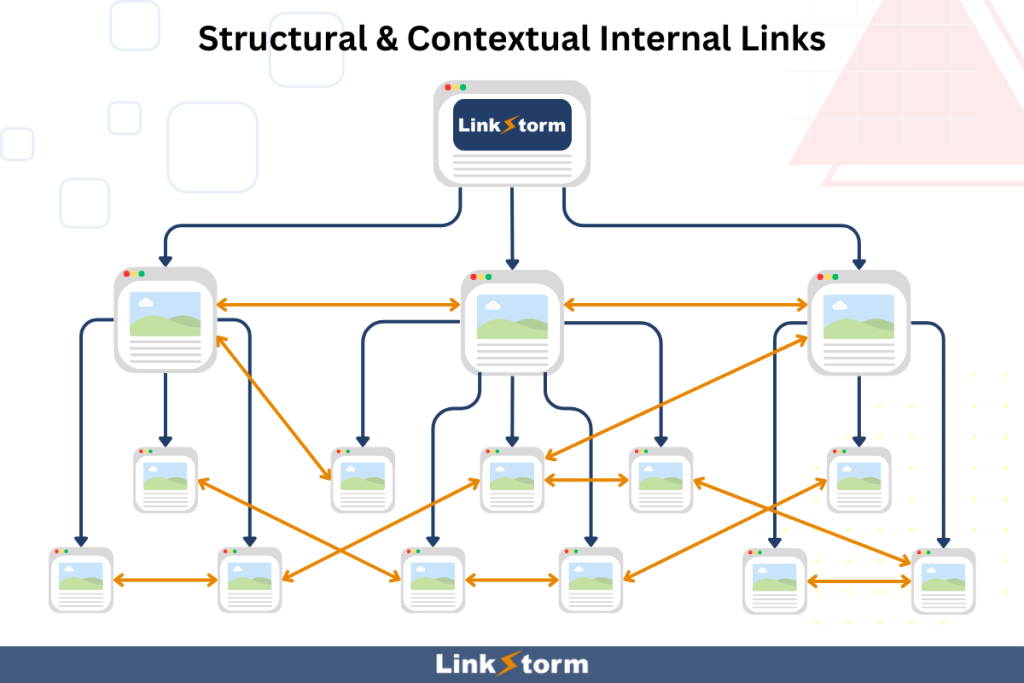
Unlike structural links, contextual links guide crawlers to pages not directly accessible via the main navigation. Moreover, contextual links reduce the crawl depth of web pages, allowing Google to discover and index more pages within its allotted crawl budget.
Googlebot also considers the anchor text used in hyperlinks to provide context about the linked page. More descriptive and relevant the link text increases the relevance scores of linked pages, increasing their SERPs ranking for those keywords.
Without structural and contextual links, Googlebot cannot find and index new pages.
It’s always an advisable internal linking practice to add links from already-indexed pages to new ones. Otherwise, search engines can’t find new content, leaving you with orphan pages or pages not linked to other sections on your site.
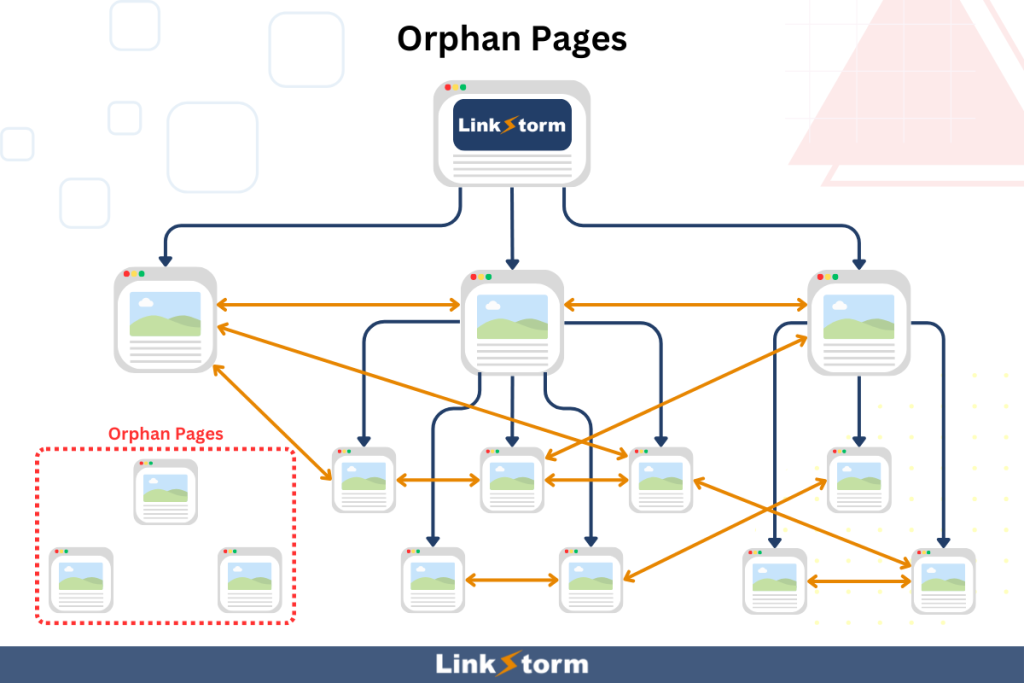
Unfortunately, many people still commit this internal linking mistake. Even the most comprehensive, high-quality, and optimized content is useless if Google can’t find it, limiting its SEO potential.
Why are Internal Links Important for SEO?
#1 Internal links pass link equity
Internal links help transfer SEO value, also known as link juice or PageRank, from the source to the target page.
PageRank is a long-standing algorithm that describes a page’s relative importance based on the quantity and quality of links pointing to it. Countless case studies validate the impact of PageRank, showing a correlation between a page’s links and its respective SERP position.
When a high-authority page links to other pages, some of its authority is shared and distributed among those linked URLs. This results in a measurable improvement in the target pages’ ranking on search results.
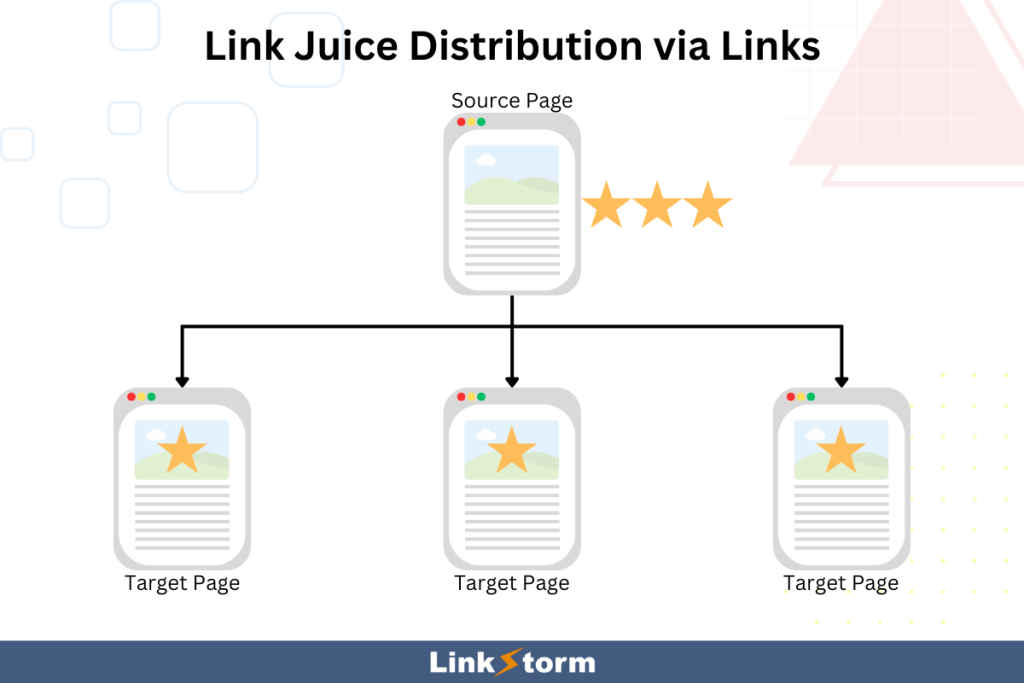
Pages with many incoming links typically rank better in SERPs, as links serve as ‘votes of confidence’ that tell Google the content is high-quality.
Since not all pages have the same authority, internal links from high-PA pages are more valuable because they transfer more link equity and are better at boosting the performance of low-PA pages.
#2 Internal links help Google understand the site structure
Imagine this:
If a website was a person, internal links are the nerves that run through the entire body. The head is the homepage since it stores the central nervous system, while the major limbs are the main category or section pages. These limbs extend out to reach the hands, feet, toes, and fingers, representing individual articles or product pages.
Nerves ensure every part of the body functions cohesively and communicates effectively with the central nervous system.
The same goes for internal links: they provide a site-wide roadmap that shows how every page is connected and related in terms of hierarchy and importance.
For example, structural links give structure to a website and describe the degree of importance of pages based on their click depth or relative proximity to the homepage.
Conversely, contextual links between pages explain to Google how those pages are interrelated.
#3 Internal links enhance crawlability & indexing
A well-linked website makes it easier for search engines to crawl and index all its pages. Internal links, especially from indexed pages, serve as passageways for the Googlebot to discover new pages.
Without links pointing to a newly published page, the page becomes orphaned. Google cannot find and add orphan pages to its large database.
Adding internal links to and from newly published content hastens the crawling and indexing process, leading to better visibility. While links without proper internal linking may eventually get indexed, it may take longer.
Note: Indexing is more than just a function of internal linking. It is necessary to publish high-quality, helpful content to increase the chances of getting into Google’s index and ranking positively on SERPs.
#4 Internal links increase page views and dwell time
Contextual links lead users to relevant content, encouraging them to explore your content more deeply.
Every click on an internal link results in an additional page view and increases session time. While page views and dwell times are no more than vanity metrics on their own, their impact on Google is much more profound.
High positive user engagement metrics inform Google that your content is worth reading, which increases your odds of ranking on SERPs.
Moreover, your marketing efforts also indirectly benefit from increased page views and dwell times, as this gives you more opportunities to persuade readers to complete a desired action, like filling out a form or completing a purchase.
Internal linking and effective marketing go hand in hand to serve your business goals.
#5 Internal links reinvigorate older content
Older website content is predisposed to become stale, especially when you neglect to update the copy or information on the content. As newer content is published, stale content will be buried deep within your website and eventually fall off SERP rankings.
Adding internal links from newer content reduces the click depth of older pages. This helps site visitors access older content, reactivating the stale page’s user engagement metrics. Of course, aside from adding internal links, updating stale content’s information is equally important.
Note: Instead of updating content every time, consider creating evergreen content. These types of content holds their value even after years.
#6 Internal links are more cost-effective than other SEO strategies
Everyone can do internal linking. Find the page you wish to target and embed its link in an appropriate anchor text in an article, and voila, you have a contextual link.
Internal linking is also free because adding internal links to a website usually doesn’t require external professional help.
In other words, internal linking is arguably the easiest and most economical SEO strategy as opposed to other link-building tactics.
For example, building backlinks requires skills in cold outreach, link-building, copywriting, and finding viable website partners. In this case, hiring a professional SEO service is better than attempting to D.I.Y. link-building.
Tips for Internal Linking for Improved SERP Performance
The power of internal linking for SEO can never be understated. When done strategically, internal links can help improve your website’s overall structure and visibility, resulting in improved search rankings.
Here are some tips to make your internal linking more effective and efficient:
1. Control the direction of internal links
Internal linking is a strategic process, and how you do it may impact your pages differently.
There are two ways to modify the direction of your internal links:
Scale-down approach
Scale-down internal linking happens when you create internal links from high-PA to low-PA pages. PageRank of high-PA pages is shared and distributed among low-PA pages, improving the latter’s ranking on search results.
Scale-up approach
Scale-up internal linking involves creating internal links between fellow high-PA pages. This approach is designed to boost the performance of already high-ranking pages further.
For example, internal links from other authoritative pages may improve a link’s SERP rank from position #2 to position #1.
2. Invest in internal linking tools
Manually finding and building internal links is tedious and time-consuming. An internal linking tool automates the process by suggesting sitewide linking opportunities. This frees up your time and energy for more critical activities.
In other words, SEO tools perform the heavy lifting, taking the strain away from you.
Every tool is different, offering unique flavors on a website. It’s advisable to read reviews and study which tool best serves your business and budget.
Looking For A Reliable Internal Linking Tool?
Powered by artificial intelligence, LinkStorm helps site owners and SEOs extract all possible internal linking opportunities on websites.
From the dashboard, simply click Opportunities from the sidebar menu.
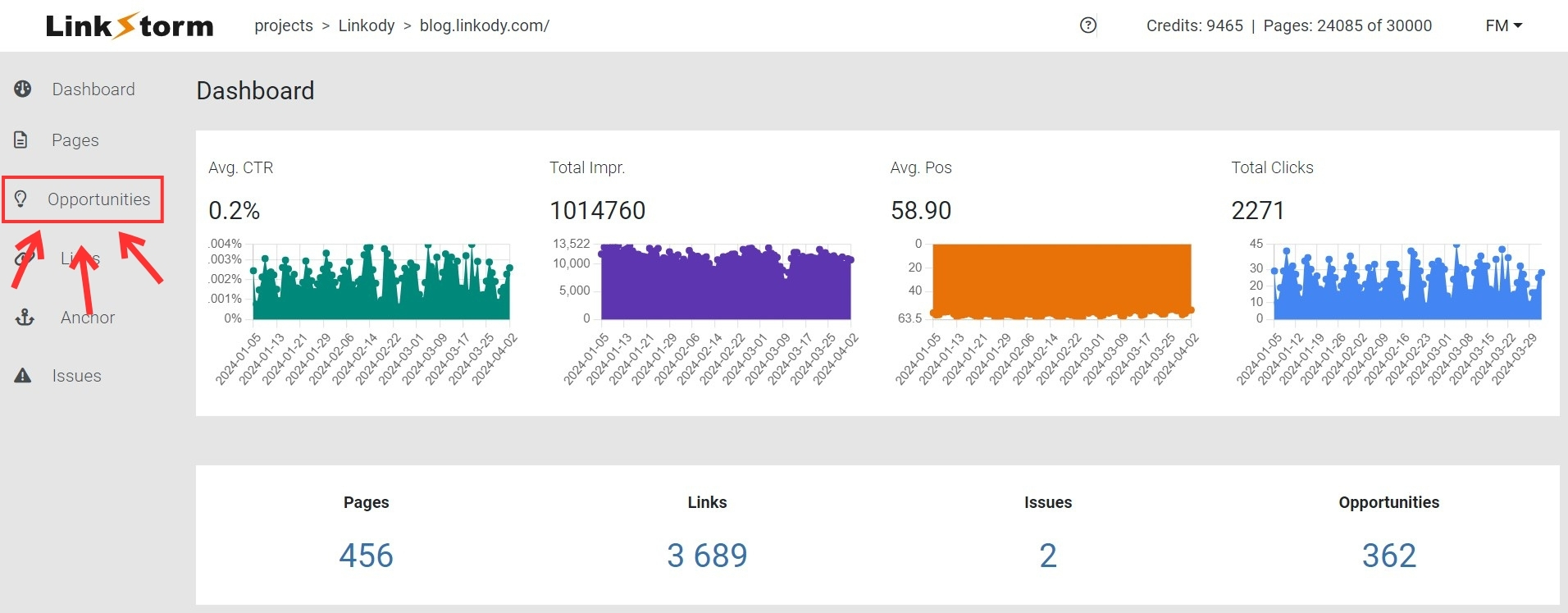
This lets users choose between two algorithms for how they want LinkStorm to find link opportunities on the website.
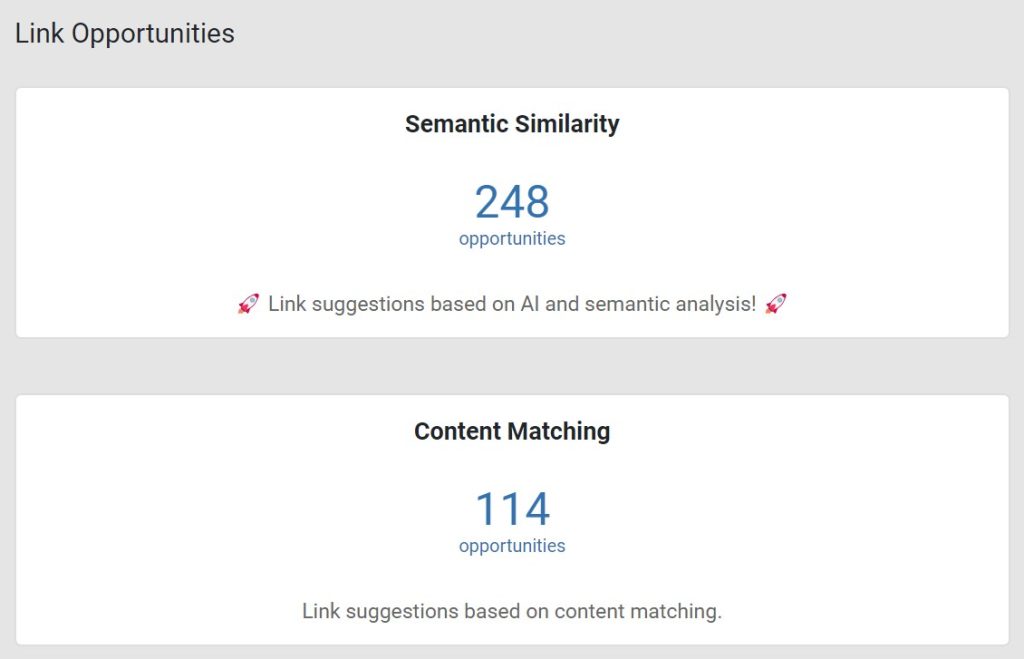
- Semantic similarity: Uses semantic analysis to understand the context behind each content, providing pertinent contextual internal links.
- Content matching: Find matching seed keywords across websites used as anchor texts for internal linking.
The tool intelligently finds contextual links on your behalf in a snap.
Here are some internal link opportunity results of LinkStorm’s semantic similarity feature:
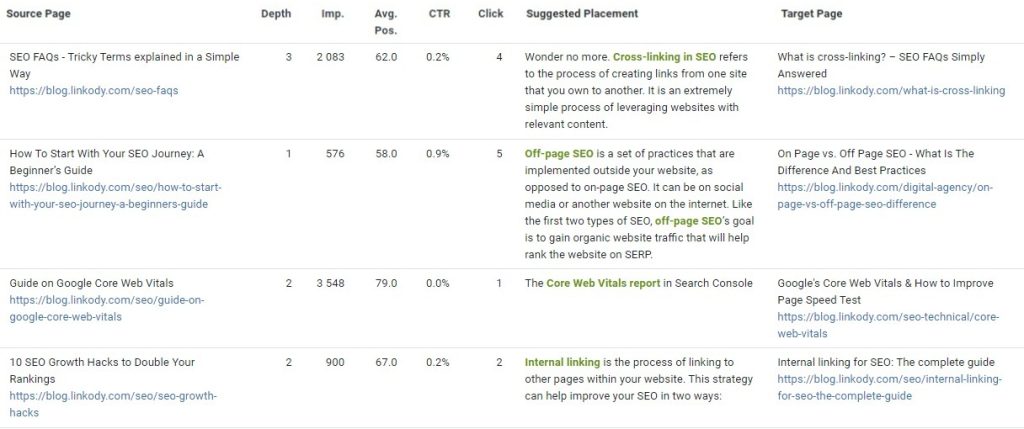
From here, users have complete control over accepting or rejecting internal link suggestions straight from the LinkStorm tool.
Aside from internal link opportunities, LinkStorm can identify site-wide linking issues, help with anchor text optimization, and reduce click depth. All of these factors serve your website’s overall search performance.
Interested?
Visit LinkStorm’s plan and pricing page to assess which option best suits your needs and try LinkStorm for FREE—no credit card required, no strings attached.
Leave a Reply