What are Broken Internal Links?
Broken internal links refer to links pointing to another page on your website that do not work or exist.
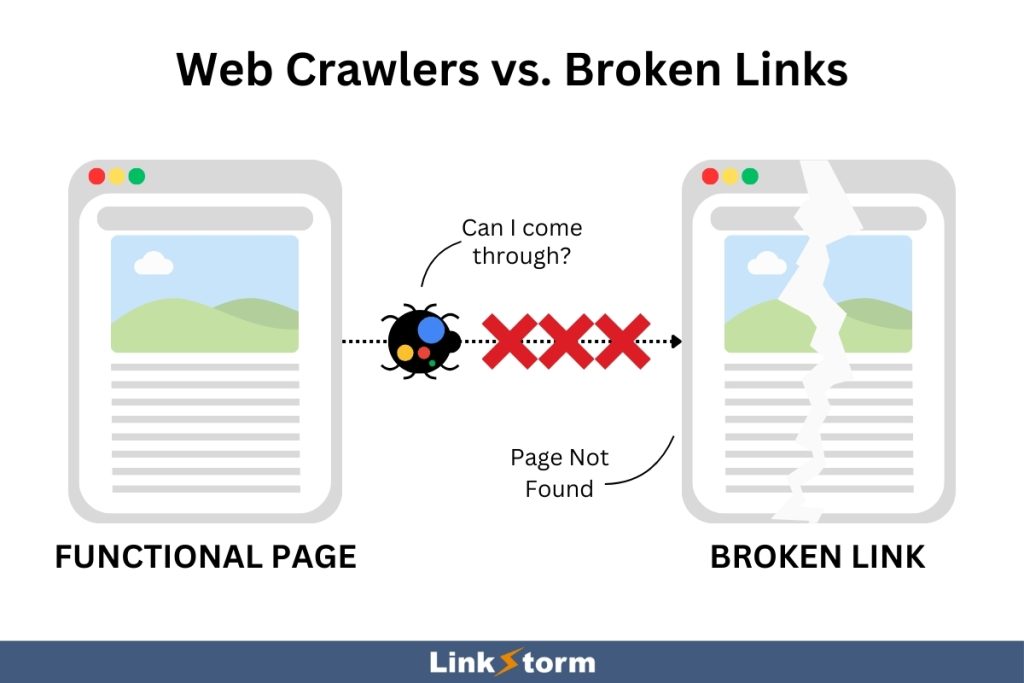
Broken links on your site can exist for many reasons. The site owner may have unconsciously moved or deleted the target page without updating the internal links.
Unfortunately, broken pages display a 404 error page that frustrates users and prevents search engine crawlers from accessing the page. This negatively impacts your SEO, affecting your pages’ performance on search engine results.
In this resource, we will focus on understanding broken internal links and uncovering how to find broken links and fix them permanently.
Causes of Broken Internal Links On a Website
As mentioned above, broken internal links on your website can occur for many reasons. Below, we have listed 5 causes behind some of your link’s pesky 404 error messages.
1. The URL used was incorrect
Inserting an incorrect URL is the simplest and most straightforward reason for a broken link. However, this simple error can greatly impact user experience and search performance.
Here are some ways you may have entered an incorrect URL:
- typo or misspelling of some words in the slug
- using double hyphens on the URL
- putting underscore instead of hyphens or dashes
- using “http://” instead of “https://” in the URL
- adding an extra space
These seemingly minor URL errors can all lead to broken internal links. They happen during content creation, so you might overlook them until you conduct your site audit.
As the adage goes, prevention is better than cure. In this case, it is better to double-check the internal links pointing to various URLs than to find broken internal links later. Before publishing new content, ensure that each internal link embedded on the page is functional.
Doing so helps fix the problem before it even happens.
2. The original page’s URL was changed
Changing URLs is a common practice, especially in SEO. Most of the time, it’s an attempt to make slugs more concise, SEO-friendly, and evergreen.
For instance, let’s say you have a page with the URL:
https://sampleseosite.com/blog/best-internal-linking-practices-in-2024
This slug might seem current in 2024 but wouldn’t be as effective for the succeeding years.
In this case, you can remove the date from the URL to keep it evergreen:
https://sampleseosite.com/blog/best-internal-linking-practices
While this seems sensible to improve SEO and CTR, it can also be a double-edged sword when left unmanaged. When no 301 redirects are added, people clicking through the internal link will still be taken to the old link instead of the new URL. This meets users with a 404 page that only ruins user experience.
To fix this, any links pointing to the old URL must be changed to the new link to prevent users from reaching a broken page.
3. The linked page was deleted from the site
Page deletion is another reason for broken links on your website. If an internal link points to a page that no longer exists, the link will be broken.
You might think, “Then I just won’t delete the page.” Sure, but countless case studies have already pointed to link decay as a serious cause of broken links. According to a case study by Linkody, almost half of all links become broken after 7 years.
Site owners may delete or remove a link without replacing it with a new page, whether consciously or not. In other words, link decay is inevitable, especially for older websites.
It’s important to actively conduct internal link audits to keep track of every page on your site. Who knows? You might be harboring many broken links from deleted pages without your knowledge.
4. The site’s content was migrated to another website
Website content is dynamic. Sometimes, entire sections or pages must be moved to a new location, like an entirely different website. This can likely be due to one of two reasons:
- Merging websites: If you’re attempting to merge two websites into one, content from the old site needs to be integrated into the new structure. This can lead to broken internal links if the old content isn’t mapped to their new corresponding pages on the new website.
- Moving to a new domain: If you migrate your entire website to a new domain name, all your internal links will break if not updated to reflect the new domain.
In this case, you may either implement a 301 redirect from the old pages or replace the old links entirely with the new ones.
5. The website URL structure was updated
Content migration from one domain to another is not always true for many websites. However, website restructuring is commonplace for older websites, especially if site owners want to properly organize them effectively.
For instance, let’s say your blogs used to be connected to your website’s root directory or homepage:
https://www.example.com/this-is-an-example-blog
But given the growing number of articles on your website, you moved all resources to a dedicated subfolder:
https://www.example.com/resources/this-is-an-example-blog
All internal links pointing to the original URL will be broken. Like all other broken links, you must add a 301 redirect to resolve the issue or replace the internal link entirely. Otherwise, the link will ruin the user experience. Google might also remove the link from its index.
Why Are Broken Links Bad for Internal Linking Campaigns?
We’ve already established that internal links are an important part of SEO. First, they drive referral traffic to your website’s important pages. Second, they speed up web crawlers’ crawling and indexing process. However, broken links can impede the effectiveness of internal links.
While we’ve mentioned a few above, below, we’ll look at more reasons why broken links can adversely affect SEO. Keep reading.
Reason #1: Creates a negative user experience
Internal links are designed to take users from one page to another related page to satisfy their search journey.
Conversely, broken links can frustrate users. Instead of reaching pages that answer their search inquiry, they are met with 404 error responses.
This negatively impacts the user experience, sometimes forcing users to opt-out or exit the website. Unfortunately, a user’s activity on a website sends signals to Google and informs the search engine whether the site is helpful or not.
A surge in a website’s bounce rate may tell Google that the content isn’t helpful, resulting in a decrease in SERP ranking. In other words, broken internal links may indirectly impact a website’s SEO performance.
Reason #2: Limits the crawlability of web crawlers
Google uses internal links as portals to crawl your website. So long as internal links work, the web crawler can freely explore a site’s internal linking structure, indexing new pages along the way.
Broken links, however, appear as dead ends in a web crawler’s journey, stopping them from fully navigating a website.
If you have a well-connected site, one broken link may not be enough to paralyze the Googlebot from crawling all pages. However, it becomes a worse problem if the broken link is the only bottleneck preventing web crawlers from reaching all other pages.
For example, a site owner mistakenly embedded an incorrect URL of the website’s blog subdomain on the homepage. That means users will always reach a 404 error page when clicking blog from the website’s main navigation panel.
In that case, the web crawler cannot crawl a website’s entire blog archive. Every new post you publish will remain hidden from Google’s eyes, never reaching the search engine’s index.
Reason #3: Prevents link juice effective distribution across pages
Like other link-building approaches, internal linking can transfer link juice from the source to the target page. With effective internal linking, pages can effectively distribute their authority across all web pages. This results in a collective boost in SEO performance and a measurable increase in SERP ranking.
However, broken links can impede the transfer of link equity from a linking page, greatly limiting a website’s SEO potential. Instead of equally dividing the link juice among functional internal links, link juice is distributed across all links, broken or not, as shown below:
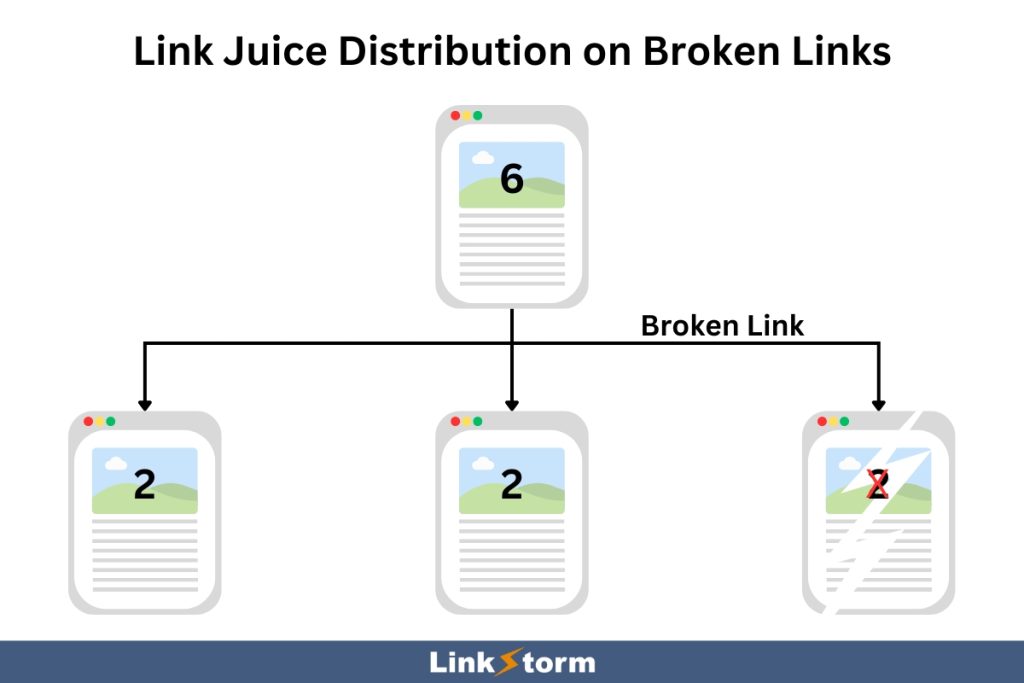
In other words, some of the source page’s link juice is wasted when broken links are present. This limits functional pages from maximizing the amount of link juice they receive.
So, it begs the question: How can site owners find and fix broken internal links on their websites?
How to Find and Fix Broken Internal Links?
The Manual Approach
You cannot tell which internal links are broken or functional at face value. The manual approach involves visiting every page and clicking the links to see where they take you.
If they lead to the intended page as indicated by their anchor texts? Well and good!
If it takes you to a web page that looks like this? You have a broken link on your hands:
The next step is to fix those broken links. Remove the link entirely on your CMS and replace it with the correct URL. This will ensure your links work properly, taking users to the intended page and helping web crawlers explore your website effectively.
Just repeat the process throughout all your web pages until all broken links are dealt with. It’s a slow yet no-nonsense process for removing the broken links persisting on your website.
If you’re looking for a quick and easy solution, LinkStorm is the best option.
The Automatic Process Using LinkStorm
LinkStorm is an all-in-one internal linking toolkit designed to help site owners and SEOs elevate their internal linking campaigns. The software is equipped with web crawlers that automatically review all pages on a website, finding internal linking gaps and uncovering internal link issues, including broken links.
Here’s how you can do it:
From the LinkStorm dashboard, click the Issues tab.
Then, select the Broken tab from the three options: No Follow, Broken, and Redirected.
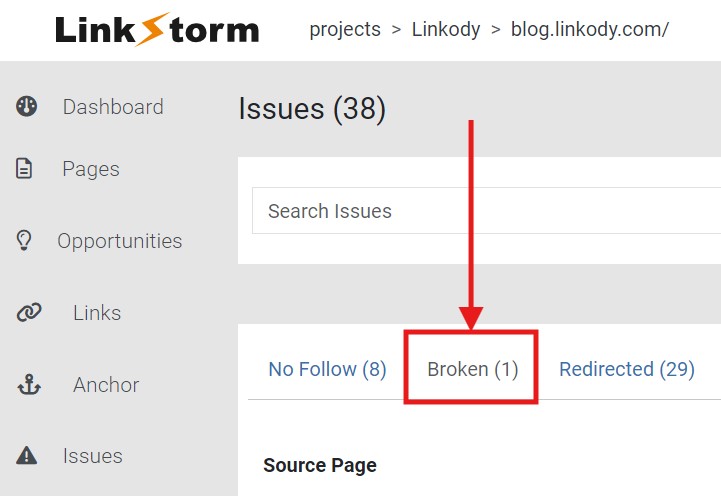
As shown below, this will show all of the broken links throughout your website, including the Source Page, Target URL, and Status Code.
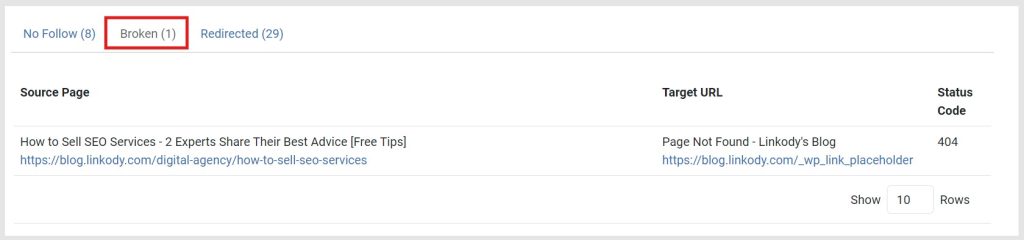
You can then check the website via your CMS and replace the broken link with the correct one.
Instead of manually visiting all web pages, LinkStorm can review the website and look for broken links for you. This saves you valuable time versus pursuing a manual approach. It is safe to presume that you will save more resources by investing in a specialized tool like LinkStorm than by doing it manually.
Key Takeaways
Keeping broken links on a website is never a good idea. They only ruin the user experience, prevent the Googlebot from crawling and indexing pages, and limit the website’s ability to achieve its maximum SEO potential.
While site owners can always manually find and fix broken internal links, this approach will be more time-consuming. Instead of saving money versus investing in internal linking software, a manual approach to fixing broken links is more resource-intensive in the long run.
This is where LinkStorm comes in.
LinkStorm is a specialized internal linking toolkit designed to help site owners stay ahead of their internal linking efforts. From suggesting internal link opportunities to fixing broken links on a website, this tool is a must-have for site owners and SEOs alike!
Check LinkStorm’s pricing page to find which plan best suits your business.
Leave a Reply